http://www.nytimes.com/2015/04/24/world/asia/drone-strikes-reveal-uncomfortable-truth-us-is-often-unsure-about-who-will-die.html
APRIL 23, 2015
Drone Strikes Reveal Uncomfortable Truth: U.S. Is Often Unsure About Who Will Die
By SCOTT SHANE
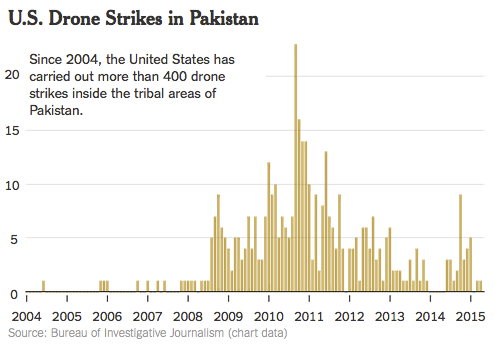
Barack Obama inherited two ugly, intractable wars in Iraq and Afghanistan when he became president and set to work to end them. But a third, more covert war he made his own, escalating drone strikes in Pakistan and expanding them to Yemen and Somalia.
The drone's vaunted capability for pinpoint killing appealed to a president intrigued by a new technology and determined to try to keep the United States out of new quagmires. Aides said Mr. Obama liked the idea of picking off dangerous terrorists a few at a time, without endangering American lives or risking the yearslong bloodshed of conventional war.
"Let's kill the people who are trying to kill us," he often told aides.
By most accounts, hundreds of dangerous militants have, indeed, been killed by drones, including some high-ranking Qaeda figures. But for six years, when the heavy cloak of secrecy has occasionally been breached, the results of some strikes have often turned out to be deeply troubling.
Every independent investigation of the strikes has found far more civilian casualties than administration officials admit. Gradually, it has become clear that when operators in Nevada fire missiles into remote tribal territories on the other side of the world, they often do not know who they are killing, but are making an imperfect best guess.
The president's announcement on Thursday that a January strike on Al Qaeda in Pakistan had killed two Western hostages, and that it took many weeks to confirm their deaths, bolstered the assessments of the program's harshest outside critics. The dark picture was compounded by the additional disclosure that two American members of Al Qaeda were killed in strikes that same month, but neither had been identified in advance and deliberately targeted.
In all, it was a devastating acknowledgment for Mr. Obama, who had hoped to pioneer a new, more discriminating kind of warfare. Whether the episode might bring a long-delayed public reckoning about targeted killings, long hidden by classification rules, remained uncertain.
Even some former Obama administration security officials have expressed serious doubts about the wisdom of the program, given the ire it has ignited overseas and the terrorists who have said they plotted attacks because of drones. And outside experts have long called for a candid accounting of the results of strikes.
"I hope this event allows us at last to have an honest dialogue about the U.S. drone program," said Rachel Stohl, of the Stimson Center, a Washington research institute. "These are precise weapons. The failure is in the intelligence about who it is that we are killing."
Ms. Stohl noted that Mr. Obama and his top aides have repeatedly promised greater openness about the drone program but have never really delivered on it.
In a speech in 2013 about drones, Mr. Obama declared that no strike was taken without "near-certainty that no civilians will be killed or injured." He added that "nevertheless, it is a hard fact that U.S. strikes have resulted in civilian casualties" and said "those deaths will haunt us as long as we live."
But over the Obama presidency, it has become harder for journalists to obtain information from the government on the results of particular strikes. And Mr. Obama's Justice Department has fought in court for years to keep secret the legal opinions justifying strikes.
Micah Zenko, a scholar at the Council on Foreign Relations and lead author of a 2013 study of drones, said the president's statement "highlights what we've sort of known: that most individuals killed are not on a kill list, and the government does not know their names."
Mr. Zenko noted that with the new disclosures, a total of eight Americans have been killed in drone strikes. Of those, only one, the American cleric Anwar al-Awlaki, who joined Al Qaeda in Yemen and was killed in 2011, was identified and deliberately targeted. The rest were killed in strikes aimed at other militants, or in so-called signature strikes based on indications that people on the ground were likely with Al Qaeda or allied militant groups.
Though by most accounts seven of the eight Americans were allied with Al Qaeda, Obama administration lawyers have ruled that a special legal review should be conducted before killing Americans suspected of terrorism. Such a review, they have argued, amounts to the legal "due process" required by the Constitution, though some legal scholars do not believe such reviews meet the constitutional test.
When Americans have been killed, however, the Obama administration has found it necessary to break with its usual practice and eventually acknowledge the deaths, at least in private discussions with reporters.
That was the case in the first C.I.A. drone strike, in Yemen in 2002, which turned out to have killed an American in Al Qaeda. It was the case in 2011, when an American Qaeda propagandist from North Carolina, Samir Khan, was killed along with Mr. Awlaki. And it happened two weeks later, when another American strike killed Mr. Awlaki's 16-year-old son and his 17-year-old cousin.
Military and intelligence officials said they did not know that the teenagers were present when they took a shot at a Qaeda operative who, it turned out, was not there. But such admissions, in the rare cases that officials were willing to discuss, undercut their argument that in most cases they were confident that they were killing only dangerous militants.
Most security experts still believe that drones, which allow a scene to be watched for hours or days through video feeds, still offer at least the chance of greater accuracy than other means of killing terrorists. By most accounts, conventional airstrikes and ground invasions kill a higher proportion of noncombatants. But without detailed, reliable, on-the-ground intelligence, experience has shown, drones make it possible to precisely kill the wrong people.
Mr. Zenko said that an average of separate counts of American drone strikes by three organizations, the New America Foundation, the Bureau of Investigative Journalism and The Long War Journal, finds that 522 strikes have killed 3,852 people, 476 of them civilians. But those counts, based on news accounts and some on-the-ground interviews, are considered very rough estimates.
The proliferating mistakes have given drones a sinister reputation in Pakistan and Yemen and have provoked a powerful anti-American backlash in the Muslim world. Part of the collateral damage in the strikes has been Mr. Obama's dream of restoring the United States' reputation with Muslims around the globe.
Despite the bad reviews overseas, drone strikes remain persistently popular with the American public, with about two-thirds expressing approval in polls. And despite the protests of a few liberal Democrats or libertarian Republicans, they have enjoyed unusual bipartisan support in Congress, where they are viewed as reducing the threat of terrorist attack and keeping American operators out of harm's way.
Mr. Zenko said that Mr. Obama and Congress should create a commission to examine the targeted killing program, its results and its flaws. But he said the combination of public and Congressional popularity probably mean that even the latest disclosures will not bring such scrutiny to the program.
"I predict that even this episode will have no effect," he said.
Matt Apuzzo and Matthew Rosenberg contributed reporting.